Which Potential Energy Diagram Represents The Change In Potential Energy That Occurs When A Catalyst
Learning Objectives
- Draw and label a potential energy diagram for a two-footstep reaction.
- Depict the use of a potential energy diagram for identifying the rate-limiting pace in a multi-step reaction.
Roller coasters-fun or frightful?
 Roller Coaster. From Greg Bulla (Wikipedia: Gb1).
Roller Coaster. From Greg Bulla (Wikipedia: Gb1).
For many people, a roller coaster is the prototype of excitement, while for others information technology is a torture device to be avoided at all costs (and some folks are in-between). For a roller coaster, the rate-limiting step is the climb upwards to the top at the beginning of the ride, where the cars are hauled slowly to the peak of the ride. This peak must be the highest because the potential energy at this indicate must be enough to cause the roller coaster to move through the smaller peaks without stopping.
Potential Energy Diagrams
The potential energy diagram can illustrate the mechanism for a reaction past showing each elementary step of the reaction with distinct activation energy (come across Effigy below ).
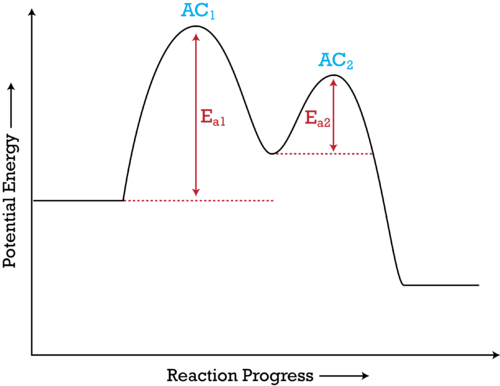 Figure i. The potential energy diagram shows an activation energy peak for each of the elementary steps of the reaction. The valley between represents the intermediate for the reaction. From the CK-12 Foundation - Christopher Auyeung.
Figure i. The potential energy diagram shows an activation energy peak for each of the elementary steps of the reaction. The valley between represents the intermediate for the reaction. From the CK-12 Foundation - Christopher Auyeung.
The reaction whose potential energy diagram is shown in the effigy is a two-step reaction. The activation energy for each step is labeled E a1 and Due east a2 . Each uncomplicated step has its own activated complex, labeled AC 1 and AC 2 . Note that the overall enthalpy modify of the reaction ![]() is unaffected by the individual steps, since it depends only on the initial and final states.
is unaffected by the individual steps, since it depends only on the initial and final states.
In this instance, the rate-limiting step in the reaction is the starting time stride, leading to the formation of the activated circuitous AC i . The activation energy is college for this step than for pace two, which has a considerably lower activation energy. If the rate-limiting stride were the second step, the peak labeled AC 2 would be college than the tiptop for AC 1 and E a2 would be greater than E a1 . The same arroyo can be taken for a potential energy diagram with more than than two peaks.
Summary
- A potential energy diagram for a 2-footstep reaction is shown and labeled.
Practice
View the section on two-step reactions at the site below and then do the cocky-examination (both buttons are at the top of the slide). Don't worry about ![]() – merely consider it an indication of activation energy as is
– merely consider it an indication of activation energy as is ![]() in the diagram above.
in the diagram above.
http://www.wfu.edu/chem/courses/energydiagram/alphabetize.html
Review
- What does a potential free energy diagram tell us?
- In the diagram above, which footstep has the highest activation energy?
- If a goad lowered the stride i activation energy to a value lower than the footstep two activation energy, which step would be rate-limiting?
Licenses and Attributions
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/cheminter/chapter/mechanisms-and-potential-energy-diagrams/
Posted by: kintzelsishomistend.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Which Potential Energy Diagram Represents The Change In Potential Energy That Occurs When A Catalyst"
Post a Comment